
I guess one would have to try, but since chances are good that I'm completely on the wrong track, I thought I better ask you guys first :-). OK -), my qestion is: Do you think it would be possible to achieve the same effect using PWM on the Arduino? What I mean is, if I put out a PWM signal of 2V and "slowly" (well, over the period of - say - 300ms) increase that signal up to the nominal 5v, do you think that would help against the audible crackling? Apparently, this reduces the "plop", because the mechanical switch inside the relay is attracted with less "force" and thus doesn't bounce back as much. Select the standard values of the resistors R1 and R2 to provide the current flowing through each LED of about 10-15 mA.
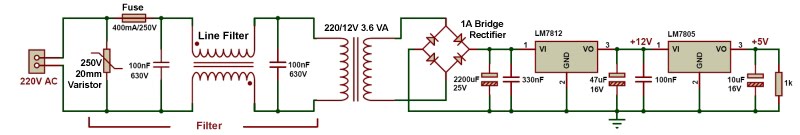
#COMPARATOR RELAY CIRCUIT FULL#
As far as I have understood the circuit, the capacitor slows down the switching signal so that the relay coil is increasingly building up its magnetic field (instead of getting the full nominal voltage at once). Specify the pin connection number of the opamp IC on the schematic symbol for use as a voltage comparator. I have seen a circuit that tries to avoid this by using a capacitor/resistor/transistor combination to drive a relay. The problem is that relays have a bad habit of "bouncing" (is that the correct english term?), thus producing an audible "plop". Either I have damaged the comparator IC by reversing the polarity (which I'm quite sure I haven't) or all 3 IC that I have purchased are faulty.As I said above, I'm planning to switch low-impedance signals (from passive guitar pickups) using relays.

Have taken this into consideration when troubleshooting the comparator circuit but still, no positive results. I am aware of the transistor usage for switching on and off the relay. Ii) The relay is electromagnetic type.Dear Mr/Mrs grsalvi, GrsalviI cant help you much with comparator and transistor part,but as far as Note :i) don't search for label 5, i skipped it by mistake.😉
#COMPARATOR RELAY CIRCUIT FREE#
If this concept fits with your project and you have doubts ,feel free to ask here.😀 In Our case we would give it through PLC.į) You can use anything to supply a small signal enough to turn ON transistor.į) As base of transistor gets signal,transistor current flows and the relay coil circuit (2) gets The transistor is labeled (3).ĭ) So ultimately, you can control relay by switching ON or OFF transistor (3).Į) You have to give a small signal to base of Transistor (3), to turn it ON or OFF. Input a voltage compared with the reference voltage (reference voltage through precision multi-turn potentiometer partial pressure get),the input voltage is greater than the reference voltage, the relay pull, the circuit connected, at the same time the work of the. There are three versions of 5V / 12V / 24V optional.

#COMPARATOR RELAY CIRCUIT HOW TO#
Ĭ) Now how to control closing and opening of relay switch (6) ?įor that a transistor is connected in series with relay coil (2). Channel difference is small, more accurate, 0.1V resolution accuracy. Whenever a 12V DC is fed into this coil (2) ,the relay switch (6) is closed ,henceĬlosing circuit and completing the main circuit (which you connected to point B and point A). Prince.I cant help you much with comparator and transistor part,but as far asĪ) The point B and point A of relay is connected to circuit which you want to controlī) Through point 1 ,we feed DC voltage which energies coil of relay labeled number 2. Can it be done? Does the parameter of input common mode voltage range affect my application? I'm guessing it does, meaning I need to use a voltage divider to drop both input and reference voltage to below 24V? Any help is appreciated. I planned to use LM393 and provide it with the same 24V reference as supply. I have a project currently requiring to compare a voltage to 24V reference and it must trigger a relay output when the input voltage is lower than 24V reference.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
